◊
◊
◊
◊

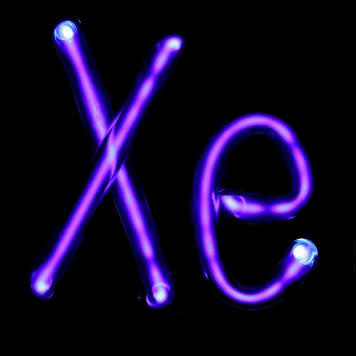

| Xe | Z = 54 | ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ |
Xenon | |
| From the Greek "xenos", meaning "foreign" | ||||
| (AM) Atomic Mass | 131.29 amu | ♦ | +2, +4, +6 | |
| -107 °C | ♦ | -112 °C | ||
| 0.005887 g/cm3 | ♦ | Face Centered Cubic | ||
| n/a | ♦ | 1.3 Å | ||
| Gas | ♦ | (C) Heat Capacity | 0.158 J/g °C | |
| Electronic-Config | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 | ♦ | 1170.36 kJ/mol | |
| 12.64 kJ/mol | ♦ | 2.27 kJ/mol | ||
| 1898 | ♦ | United Kingdom | ||
| (E°) Standard Potential | [HXeO6]3- + 5 H2O⇔ Xe + 11 OH- (1.180 V) | |||
| Stable isotopes | 124Xe, 126Xe, 128Xe, 129Xe, 130Xe, 131Xe, 132Xe, 134Xe, 136Xe | |||
| Discovered/Synthesized by | Sir William Ramsay, Morris M. Travers | |||
| Natural Source | Isolated from the liquifaction of air | |||
| Common Uses | Lamps, headlights, stadium lamps, projectors, strobes, lasers, spacecraft ion engines | |||
| Other Info | First noble gas to be shown to form chemical bonds | |||
Previous Element |
 |
Next Element |
||
| Back to Table |
Common Properties |
|||
| Home Page |
Definitions |
|||