◊
◊
◊
◊

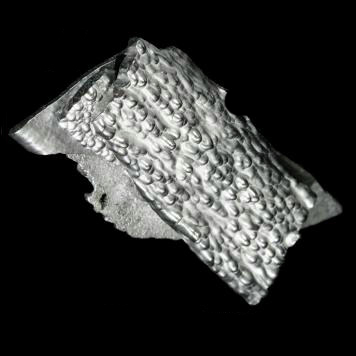

| Cr | Z = 24 | ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ |
Chromium | |
| From the Greek "chroma", meaning "color" | ||||
| (AM) Atomic Mass | 51.996 amu | ♦ | +2, +3, +6 | |
| 2672 °C | ♦ | 1857 °C | ||
| 7.14 g/cm3 | ♦ | Body Centered Cubic | ||
| 1.6 | ♦ | 1.27 Å | ||
| Solid | ♦ | (C) Heat Capacity | 0.449 J/g °C | |
| Electronic-Config | [Ar] 3d5 4s1 | ♦ | 652.82 kJ/mol | |
| 339.5 kJ/mol | ♦ | 21 kJ/mol | ||
| 1774 | ♦ | France | ||
| (E°) Standard Potential | Cr3+⇔ Cr2+ (-0.420 V), Cr3+⇔ Cr (-0.740 V) | |||
| Stable isotopes | 50Cr, 52Cr, 53Cr, 54Cr | |||
| Discovered/Synthesized by | Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin | |||
| Natural Source | The mineral/ore chromite | |||
| Common Uses | Stainless steel, kitchenware, nichrome heaters, car trim, paints, recording tape | |||
| Other Info | Compounds include numerous pigments including chrome yellow | |||
Previous Element |
 |
Next Element |
||
| Back to Table |
Common Properties |
|||
| Home Page |
Definitions |
|||