◊
◊
◊
◊
Its global supply is in critical shortage

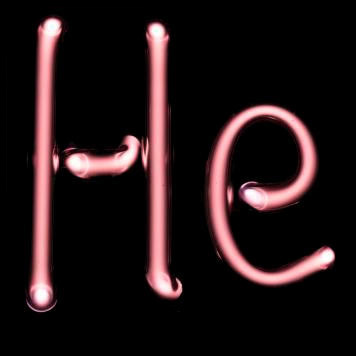

| He | Z = 2 | ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ ◊ |
Helium | |
| From the Greek "helios", meaning "sun" | ||||
| (AM) Atomic Mass | 4.0026 amu | ♦ | 0 | |
| -268.9 °C | ♦ | -272.2 °C | ||
| 0.000178 g/cm3 | ♦ | Hexagonal | ||
| n/a | ♦ | n/a | ||
| Gas | ♦ | (C) Heat Capacity | 5.193 J/g °C | |
| Electronic-Config | 1s2 | ♦ | 2372.28 kJ/mol | |
| 0.0829 kJ/mol | ♦ | 0.0138 kJ/mol | ||
| 1895 | ♦ | London | ||
| (E°) Standard Potential | Inert | |||
| Stable isotopes | 3He, 4He | |||
| Discovered/Synthesized by | Pierre-Jules-CÚsar Janssen | |||
| Natural Source | Isolated from the fractional distillation of natural gas | |||
| Common Uses | Balloons, lasers, supercold refrigerant, cooling of MRI detectors | |||
| Other Info | Smallest element Its global supply is in critical shortage |
|||
Previous Element |
 |
Next Element |
||
| Back to Table |
Common Properties |
|||
| Home Page |
Definitions |
|||